Ann Clin Microbiol 2020;23:33-43. Season and Temperature Effects on Bloodstream Infection Incidence in a Korean Tertiary Referral Hospital
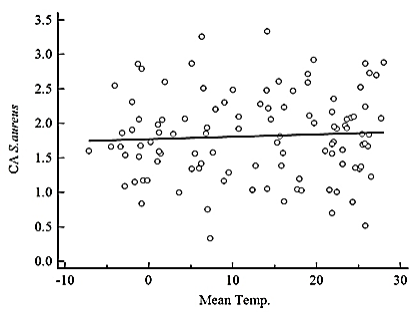
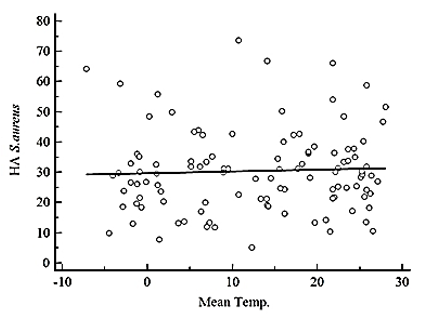
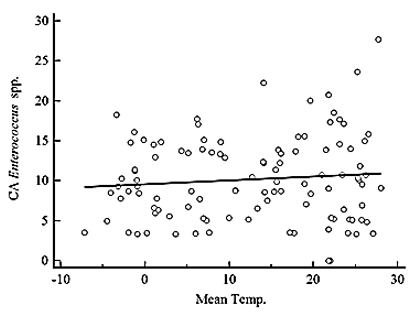
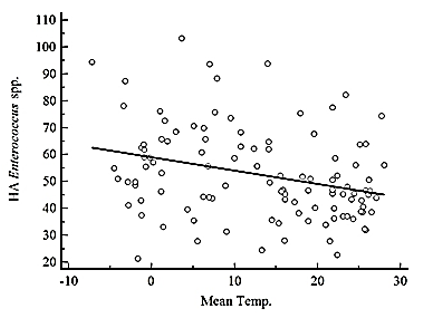
Fig. 1. Correlation between bloodstream infection (BSI) by gram-positive cocci and average monthly temperature from 2008–2016 based on Pearson’s correlation coefficient. (a) Temperature (°C) vs. incidence rate of community-onset BSI by S. aureus (cases per 105 patient days), y = 0.00337x+1.774, r = 0.0565, P = 0.5612. (b) Temperature (°C) vs. incidence rate of hospital-acquired BSI by S. aureus (cases per 106 patient days), y = 0.0588x+29.781, r = 0.0444, P = 0.6484. (c) Temperature (°C) vs. incidence rate of community-onset BSI by Enterococcus spp. (cases per 105 patient days), y = 0.0488x+9.558, r = 0.0952, P = 0.3273. (d) Temperature (°C) vs. incidence rate of hospital-acquired BSI by Enterococcus spp. (cases per 106 patient days), y = -0.495x+59.061, r = -0.3020, P = 0.0015. CA, community-onset; HA, hospital-acquired; Temp., temperature.