Figures & Tables
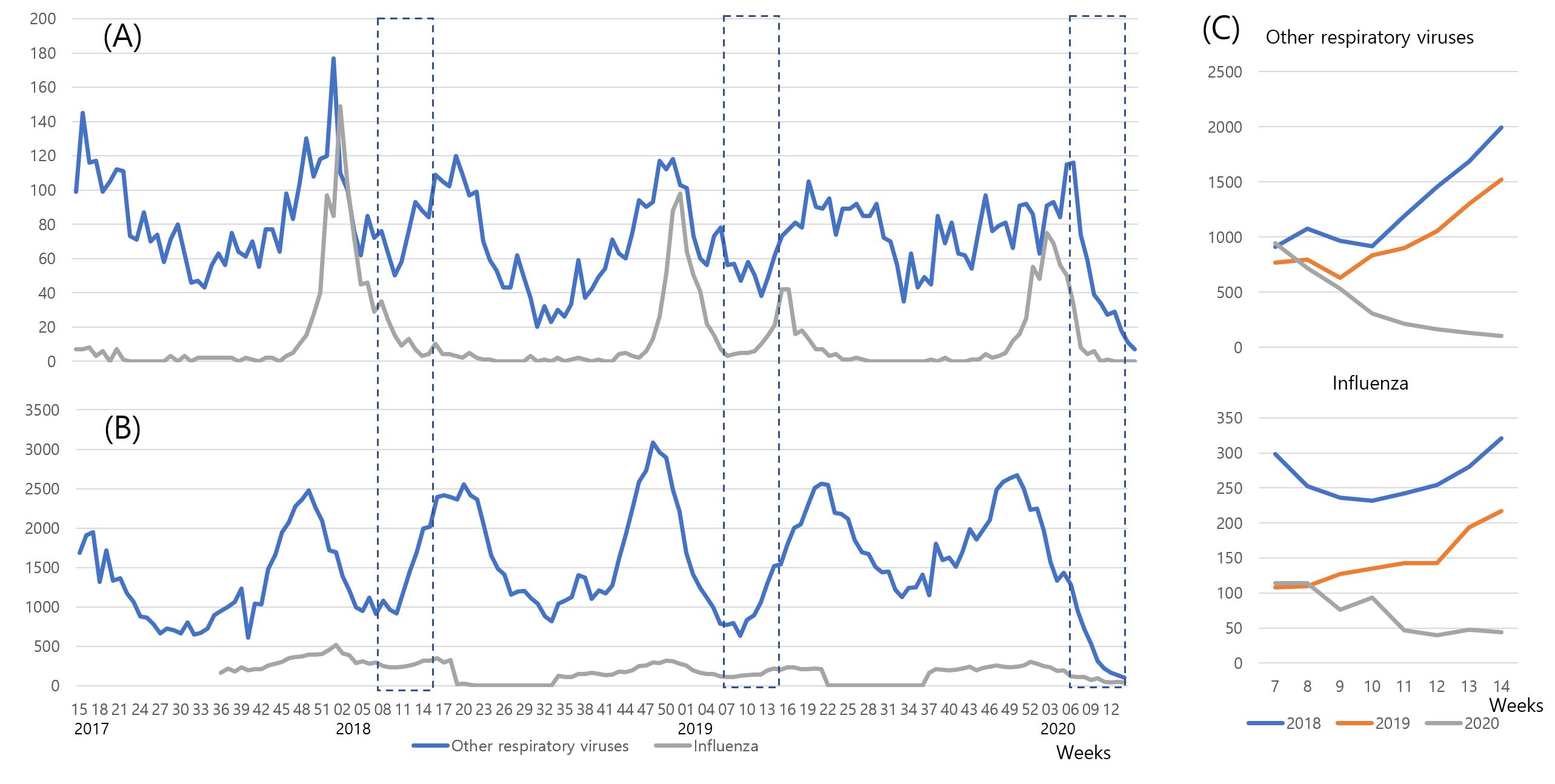
Fig. 1. (A) Number of positive cases according to the respiratory virus panel testing results of the institution, (B) Number of patients with acute respiratory viral infection as per the nationwide surveillance system (NSS) in South Korea, and (C) Comparison of the number of patients with other respiratory viruses and influenza (7th‒14th week) based on 3 year data retrieved from NSS. Dotted rectangles highlight 7th‒14th week of each year. “Other respiratory viruses” comprise adenovirus, bocavirus, coronavirus, metapneumovirus, parainfluenza virus, respiratory syncytial virus, and rhinovirus.


