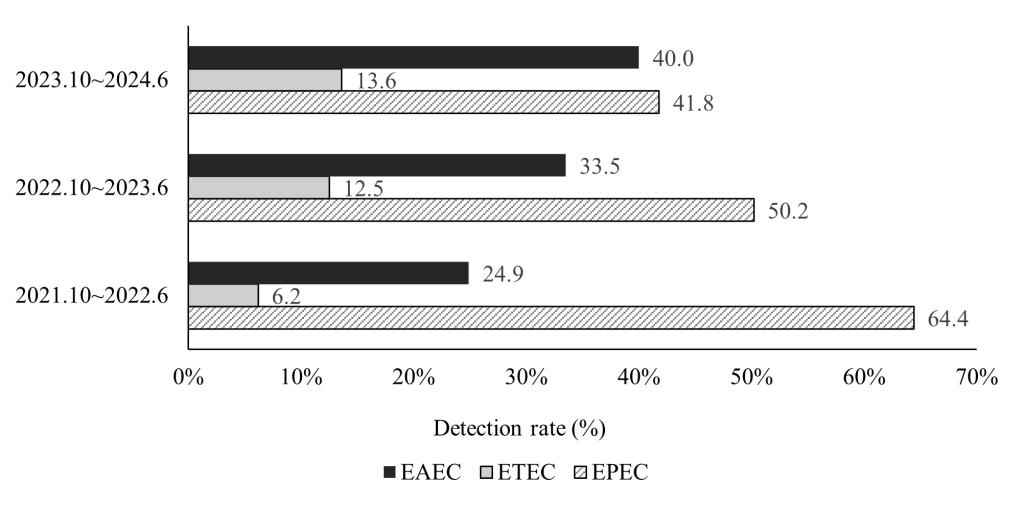
Fig. 1. Temporal trends in the prevalence of pathogenic Escherichia coli pathotypes (October 2021–June 2024). EAEC, enteroaggregative Escherichia coli; EPEC, enteropathogenic Escherichia coli; ETEC, enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli.
Ann Clin Microbiol 2025;29(1):4. Antibiotic resistance patterns of pathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from southeastern Korean patients with acute diarrhea from October 2023 to June 2024: a cross-sectional surveillance study Download image
Table 2. Comparison of antibiotic resistance and multidrug resistance rates among pathogenic Escherichia coli pathotypes
Ann Clin Microbiol 2025;29(1):4. Antibiotic resistance patterns of pathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from southeastern Korean patients with acute diarrhea from October 2023 to June 2024: a cross-sectional surveillance study Download table Variables EAEC (n = 86) EPEC (n = 67) ETEC (n = 31) Antibiotic resistance rates, n (%) AMP 81 (94.2) 40 (59.7) 20 […]
Table 3. Comparison of antibiotic resistance and multidrug resistance rates of pathogenic Escherichia coli isolates between pediatric and adult patients
Ann Clin Microbiol 2025;29(1):4. Antibiotic resistance patterns of pathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from southeastern Korean patients with acute diarrhea from October 2023 to June 2024: a cross-sectional surveillance study Download table Variables Pediatrics (n = 120) Adults (n = 72) Antibiotic resistance rates, n (%) AMP 97 (81.0) 51 (70.4) AMC 67 (56.2) 17 […]
Table 1. Antibiotic resistance profiles of pathogenic Escherichia coli isolates (N = 192)
Ann Clin Microbiol 2025;29(1):4. Antibiotic resistance patterns of pathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from southeastern Korean patients with acute diarrhea from October 2023 to June 2024: a cross-sectional surveillance study Download table Antibiotics R (n) S (n) I (n) SDD (n) R (%) S (%) AMP 148 42 2 0 77.1 22.9 AMC 85 102 5 0 […]
Antibiotic resistance patterns of pathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from southeastern Korean patients with acute diarrhea from October 2023 to June 2024: a cross-sectional surveillance study
Original article Suyeon Jo, Byoungkuk Kim, Boyeong Kwon, Kwanghyun Kim, Minhyeok Kim, Kihyung Park Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seegene Medical Foundation, Busan, Korea Correspondence to Suyeon Jo E-mail: freedom96@naver.com; Kihyung Park E-mail: p0413@mf.seegene.com Ann Clin Microbiol 2026;29(1):4. https://doi.org/10.5145/ACM.2026.29.1.4Received on 12 January 2026, Revised on 26 February 2026, Accepted on 27 February 2026, Published on 11 […]
Fig. 3. Logarithmic reduction values of (a) carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii (CRAB) and (b) multidrug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa (MRPA) after a 5-min exposure to 40 ppm and 300 ppm of sprayed HOCl (n = 3, mean ± SD). Purified water was used as negative control. HOCl, hypochlorous acid water; LOD, limit of detection.

Ann Clin Microbiol 2026;29(1):3. Bactericidal efficacy of atomized hypochlorous acid water against carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii and multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a hospital room Download image
Fig. 2. Logarithmic reduction values of (a) carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii (CRAB) and (b) multidrug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa (MRPA) after 0, 1, 3, and 5 h of exposure to 40 ppm and 300 ppm of aerosolized HOCl (n = 3, mean ± SD). Purified water was used as negative control. HOCl, hypochlorous acid water; LOD, limit of detection.

Ann Clin Microbiol 2026;29(1):3. Bactericidal efficacy of atomized hypochlorous acid water against carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii and multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a hospital room Download image
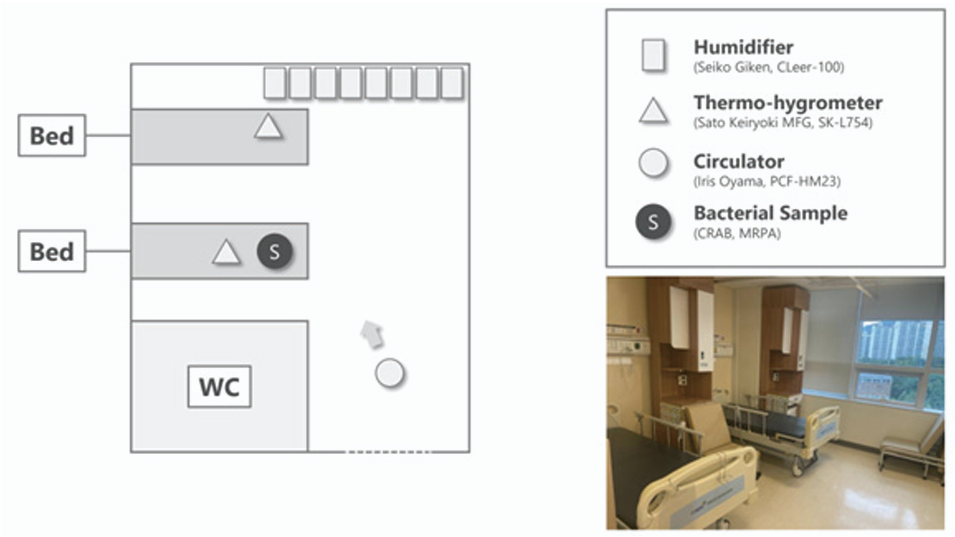
Fig. 1. Schematic representation (left) and real photography (right) of the hospital two-bed room at which the experiment was conducted. Eight humidifiers, two thermo-hygrometers, and one circulator were used for the experiment. The bactericidal effect of atomized HOCl against two bacteria, carbapenemresistant Acinetobacter baumannii (CRAB) and multidrug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa (MRPA), was evaluated. HOCl, hypochlorous acid water.

Ann Clin Microbiol 2026;29(1):3. Bactericidal efficacy of atomized hypochlorous acid water against carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii and multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a hospital room Download image
Bactericidal efficacy of atomized hypochlorous acid water against carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii and multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a hospital room
Original article Jungmi Kim1, Inyoung Kang1, Sunjoo Kim1,2 1Institute of Medical Science, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea2Department of Laboratory Medicine, GC Labs, Yangsan, Korea Correspondence to Sunjoo Kim E-mail: sjkim8239@hanmail.net Ann Clin Microbiol 2026;29(1):3. https://doi.org/10.5145/ACM.2026.29.1.3Received on 8 January 2026, Revised on 4 February 2026, Accepted on 18 February 2026, Published on 9 March 2026.Copyright © […]
Fig. 3. Correlation of toxin B gene cycle threshold values from Allplex GI-Bacteria(I) and Xpert C. difficile assays. PCR, polymerase chain reaction.

Ann Clin Microbiol 2026;29(1):1. Performance of C. Diff Quik Chek Complete and RIDASCREEN immunoassays and lack of Ct value concordance between Allplex GI-Bacteria(I) and Xpert Clostridioides difficile assays: a diagnostic accuracy study Download image
