Table 1. Historical timeline of discoveries in molecular diagnostic procedures, with descriptions and applications in the 21st century [1]
Ann Clin Microbiol 2025;28(4):22. Whole-genome sequencing applications for evolution of clinical microbiology Download table Year Molecular procedures Description Applications 2000s Microarrays Analysis of gene expression, SNP genotyping, and comparative genomic hybridization Study of gene expression, detection of genetic variation, and identification of chromosomal abnormalities 2000s Metagenomics Comprehensive analysis of entire pathogen populations Identification of rare […]
Table 2.Cycle threshold values and melt peak temperatures of Xpert MTB/RIF and Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra assays
Ann Clin Microbiol 2025;28(4):21. Impact of nontuberculous mycobacteria on the performance of Xpert MTB/RIF and Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra for the detection of tuberculosis and rifampin resistance: a diagnostic accuracy study Download table Concentration(CFU/mL equivalent) Xpert MTB/RIF Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra Ct value (1st/2nd) Ct value (1st/2nd) Tm (1st/2nd) NTM strain(1.0 × 106) MTB(5.0×103) […]
Table 1.Assessment of cross-reactivity in RIF resistance detection by Xpert and Xpert Ultra with NTM species at high bacterial load
Ann Clin Microbiol 2025;28(4):21. Impact of nontuberculous mycobacteria on the performance of Xpert MTB/RIF and Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra for the detection of tuberculosis and rifampin resistance: a diagnostic accuracy study Download table NTM strain (1.0 × 106 CFU/mL equivalent) MTB (5.0 × 103 CFU/mL equivalent) Xpert result Xpert Ultra result 1st 2nd […]
Whole-genome sequencing applications for evolution of clinical microbiology
Review article Takashi Takahashi Laboratory of Infectious Diseases, Graduate School of Infection Control Sciences and Ōmura Satoshi Memorial Institute, Kitasato University, Tokyo, Japan Correspondence to Takashi Takahashi, E-mail: taka2si@lisci.kitasato-u.ac.jp Ann Clin Microbiol 2025;28(4):22. https://doi.org/10.5145/ACM.2025.28.4.3Received on 16 September 2025, Revised on 03 November 2025, Accepted on 03 November 2025, Published on 01 December 2025.Copyright © Korean […]
Impact of nontuberculous mycobacteria on the performance of Xpert MTB/RIF and Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra for the detection of tuberculosis and rifampin resistance: a diagnostic accuracy study
Original article Sangsoo Jung1,2, Eunsang Suh1*, Jun-Ki Lee1, Byung Woo Jhun3, Tae Yeul Kim1, Hee Jae Huh1,2, Nam Yong Lee1 1Department of Laboratory Medicine and Genetics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea2Department of Medical Device Management and Research, Samsung Advanced Institute for Health Sciences & Technology, Sungkyunkwan University, Seoul, Korea3Division of […]
Fig. 2. Trends in requests for bacterial cultures and antimicrobial susceptibility tests for patients suspected of (A) pneumonia, (B) sepsis, (C) UTI, (D) soft tissue infection. N, number; UTI, urinary tract infection.
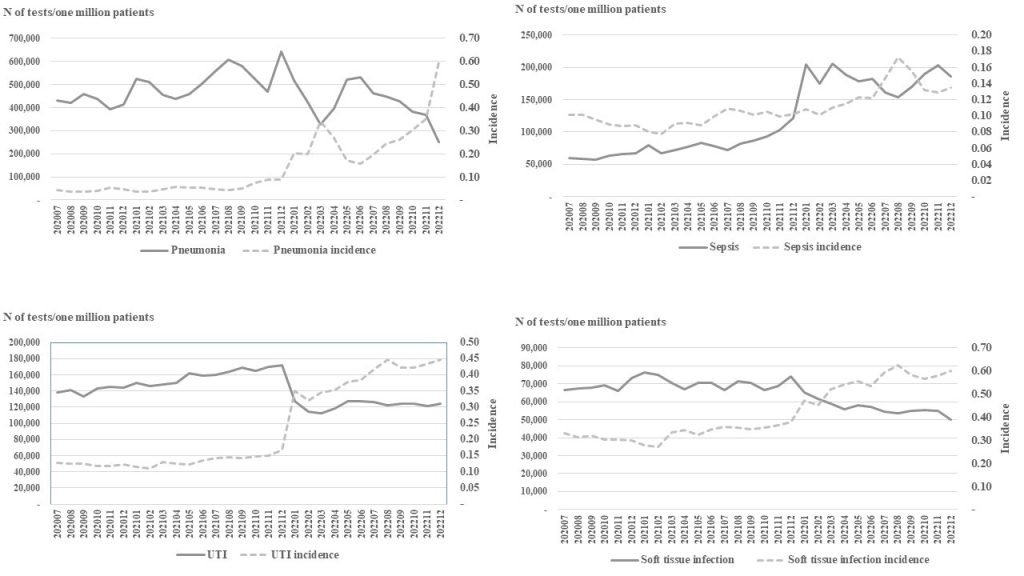
Ann Clin Microbiol 2025;28(4):20. Factors influencing microbial diagnostic testing for infectious diseases in Korea: a nationwide retrospective cohort study Download image
Fig. 1. Trends in requests for tuberculosis-related tests. N, number; AFB, acid-fast bacilli; TB, tuberculosis.

Ann Clin Microbiol 2025;28(4):20. Factors influencing microbial diagnostic testing for infectious diseases in Korea: a nationwide retrospective cohort study Download image
Table 2. Factors affecting bacterial culture and antimicrobial susceptibility tests: multivariate analysis
Ann Clin Microbiol 2025;28(4):20. Factors influencing microbial diagnostic testing for infectious diseases in Korea: a nationwide retrospective cohort study Download table Characteristics Variables Pneumonia Sepsis Urinary tract infection Soft tissue infection Total (n) Incidence rate (%) OR 95% CI P-value Total (n) Incidence rate (%) OR 95% CI P-value Total (n) Incidence rate (%) OR […]
Table 1. Factors affecting requests for tuberculosis-related tests: multivariate analysis
Ann Clin Microbiol 2025;28(4):20. Factors influencing microbial diagnostic testing for infectious diseases in Korea: a nationwide retrospective cohort study Download table Characteristics Variables Total (n) Incidence rate (%) AFB smear Mycobacterium culture Molecular diagnostic test OR 95% CI P-value OR 95% CI P-value OR 95% CI P-value Sex Male 260,824 1.01 1 – – 1 […]
Factors influencing microbial diagnostic testing for infectious diseases in Korea: a nationwide retrospective cohort study

Original article Young Ah Kim1, Jae Kwang Lee2, Hee Kyoung Choi3 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, 2Research Center, 3Department of Infectious Disease, National Health Insurance Service Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea Correspondence to Young Ah Kim, E-mail: yakim@nhimc.or.kr Ann Clin Microbiol 2025 December;28(4):20. https://doi.org/10.5145/ACM.2025.28.4.1Received on 22 July 2025, Revised on 21 October 2025, Accepted on 23 October 2025, […]
