Evaluation of Rapid Assay (Tox A/B Quik Chek) for the Detection of Clostridium difficile Toxins A and B
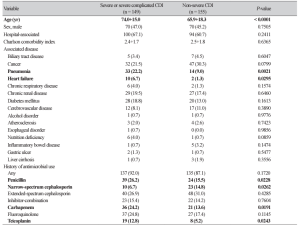
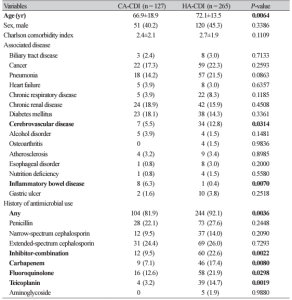
Original article PDF Sue Jung Kim1, Heejung Kim1, Myung Sook Kim1, Eunmi Koh1, Chang-Ki Kim2, Seok Hoon Jeong1, Yunsop Chong1, Kyungwon Lee1 1Department of Laboratory Medicine and Research Institute of Bacterial Resistance, Yonsei University College of Medicine; 2Korean Institute of Tuberculosis, Seoul, Korea Corresponding to Kyungwon Lee, E-mail: leekcp@yuhs.ac Ann Clin Microbiol 2008;11(2):112-116.Copyright © Korean Society of Clinical Microbiology. Abstract Background: Toxin immunoassay is widely used for rapid diagnosis of Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea. The aim of this study was to evaluate the performance of Tox A/B Quik Chek test (TECHLAB, Blacksburg, VA, USA) compared to toxigenic culture. Methods: From September 2006 to August 2007, 959 stools were examined by Tox A/B Quik Chek test and toxigenic culture (C. difficile culture plus tcdB PCR using colonies obtained from culture). Results: Compared to the results of toxigenic culture, the sensitivity and specificity of Tox A/B Quik Chek test were 47.5% and 97.5%, respectively. Conclusion: The sensitivity